How to integrate automatic doors with building access control systems?
Integrating automatic doors with building access control systems involves several key steps, from understanding the components to programming and testing the system. Here's a detailed guide:

1. Understand the Components
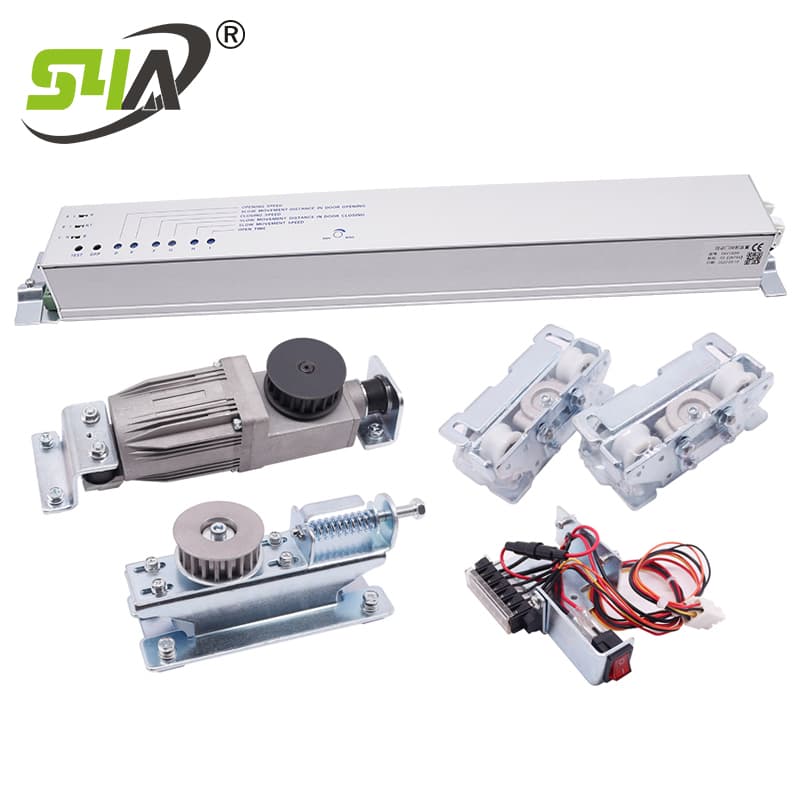
Automatic Door Operator: This is the device that controls the opening and closing of the door. It typically consists of a motor, controller, and sensors.
Access Control System: This system manages and monitors access to the building. It includes components such as card readers, keypads, biometric scanners, access control panels, and software.
2. Choose the Right Integration Method
Wired Integration: This involves connecting the automatic door operator directly to the access control system using cables. It provides a reliable and stable connection but may require more installation effort and is less flexible if you need to make changes in the future.
Wireless Integration: Utilizes wireless technologies like Bluetooth, Wi - Fi, or Z - Wave to connect the door operator to the access control system. It offers more flexibility in installation and is easier to modify or expand, but may be subject to signal interference.
3. Install and Configure the Hardware
Install the Access Control Devices: Mount the card readers, keypads, or biometric scanners at the entrances where the automatic doors are located. Connect them to the access control panel according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Connect to the Door Operator: If using a wired integration, connect the appropriate wires from the access control panel to the door operator's control inputs. For wireless integration, pair the door operator with the access control system following the wireless setup procedures.
4. Program the Access Control System
Define Access Levels: Determine who has access to the building and which doors they can access. For example, employees may have access to certain areas during working hours, while visitors may have limited access.
Set Up User Credentials: Enroll the user's information, such as card numbers, PINs, or biometric data, into the access control system. Each user should be assigned the appropriate access level.
5. Configure the Automatic Door Settings
Adjust Opening and Closing Speeds: Set the speed at which the door opens and closes to ensure smooth and safe operation. This may need to be adjusted based on the traffic flow and the type of users (e.g., slower for elderly or disabled individuals).
Set Time Delays: Determine the amount of time the door stays open after being triggered. This should be long enough for people to pass through comfortably but not so long that it affects security or energy efficiency.
6. Test and Troubleshoot
Test Access: Use the various access credentials (cards, PINs, biometrics) to test if the automatic doors open and close as expected. Check for any delays, errors, or failures in the operation.
Check Sensor Functionality: Ensure that the door sensors, such as motion sensors or infrared sensors, are working correctly. They should detect the presence of people or objects accurately to trigger the door opening.
Verify Security Features: Test the security features of the system, such as anti - tailgating mechanisms and door locking functions when access is denied.
7. Regular Maintenance and Updates
Maintain the System: Regularly check the hardware for any signs of wear or damage. Clean the card readers, sensors, and door tracks to ensure proper functioning.
Update Software and Firmware: Keep the access control system's software and the door operator's firmware up to date. Manufacturers often release updates to improve performance, fix bugs, and enhance security.
Professional installation and integration services are recommended to ensure the proper functioning and security of the system. Additionally, local building codes and regulations should be followed during the installation process.
Author: Written by Ms.Anna Zhang from S4A INDUSTRIAL CO., LIMITED